3 Tips for Managing Water Conveyance System Challenges
EXTEND THE USEFUL LIFE OF YOUR WATER CONVEYANCE ASSETS
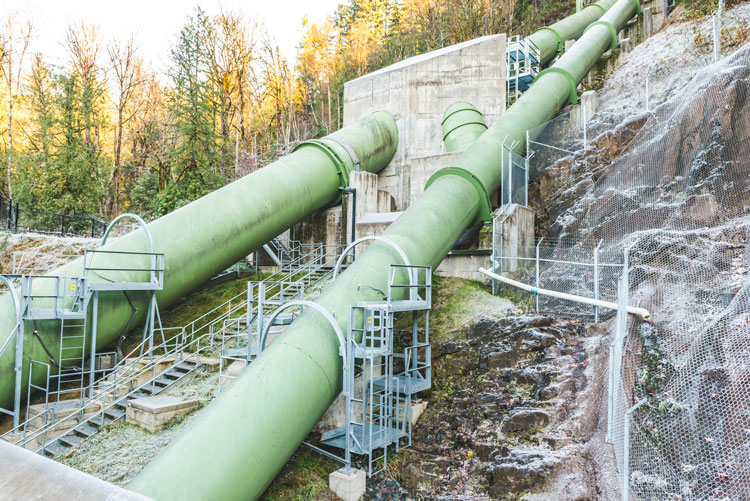
Water conveyance assets, such as headgates, tunnels, canals, and penstocks, are critical components that literally and figuratively fall between the dam and the powerhouse and sometimes fall between the cracks of asset management programs. These assets are crucial to the efficiency, reliability, and longevity of hydroelectric systems.
However, unlike dams or mechanical and electrical powerhouse equipment, water conveyance infrastructure often lacks rigorous regulatory requirements for inspection, evaluation, or refurbishment. Absent compliance requirements, unique maintenance challenges can occur. At the same time, these assets face stiff competition for funding in operating and capital budgets against assets with a more direct link to revenue generation.
Here are three essential tips to help you manage your water conveyance system challenges:
1. Know Your Assets
The first step in effectively managing water conveyance assets is comprehensively understanding them. Documenting key details is crucial. These details include:
- Locations, dimensions, materials, and vintage: Knowing exactly where each asset is located, its size, the materials it’s made from, and its age can help you prioritize inspections, evaluations, maintenance, and repairs.
- Design, fabrication, and construction practices: Understanding how the asset was designed and built can provide insights into its durability, performance capabilities, and potential weaknesses.
- Historical operating conditions and performance: Historical data can help identify patterns of wear and tear or operational stress that may need addressing.
- Current operating conditions and performance: Regularly updating this information helps ensure that your maintenance strategies are based on the latest data.
- Use remote sensing technology to identify changes: Remote sensing using laser scanning, remotely operated vehicles, or photogrammetry methods has become an increasingly important and cost-effective tool to identify and quantify changes over time.
Access to the original system design documents, fabrication drawings, and construction records is ideal. For older facilities, especially those with more than one owner, the available records can be limited or even nonexistent. However, valuable information can often be found in published papers or documents available through libraries.
For instance, I helped an owner locate original bid documents for a 1920s vintage dam at a local university library. This kind of detective work can uncover a wealth of information that can be used to understand the design intent and construction challenges better, identify conditions that may not be accurately reflected on the as-built record drawings, and inform long-term maintenance and refurbishment planning.
2. Know Your Assets’ Threats
The next step is to evaluate the critical threats to your water conveyance assets, such as penstocks or water conveyance pipelines. I like to start with the framework included in ASME 31.8S Managing System Integrity of Gas Pipelines (2018), which classifies threats into three main categories:
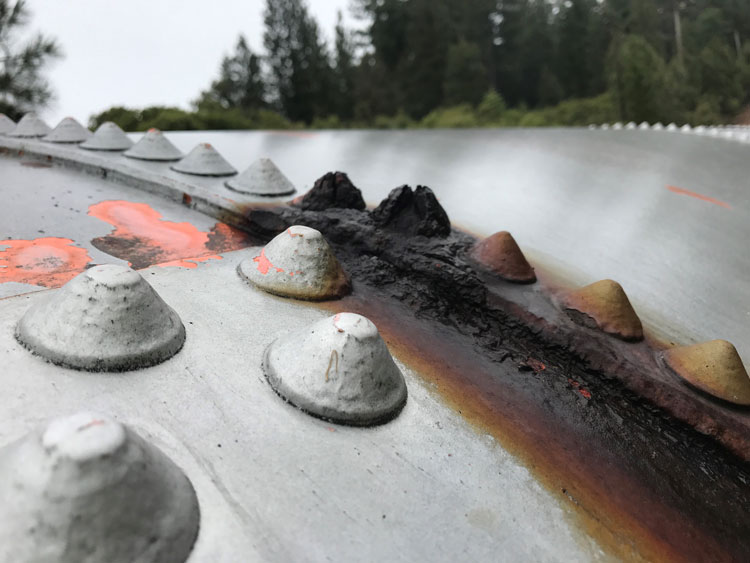
- Time-dependent threats: These threats develop over time and increase the likelihood of failure as the asset ages. Examples include internal and external corrosion and deteriorating pipeline gaskets, packing, and associated valves and equipment.
- Random or time-independent threats: These unpredictable threats can occur anytime during the asset’s life. Examples include misoperation, third-party damage, vandalism, and geotechnical or geologic threats, including earthquakes.
- Resident threats: These threats can be considered system vulnerabilities. They include manufacturing and installation defects and equipment failure. Many of these failures occur at the beginning of an asset’s life, with some, like equipment failure, continuing for the rest of the asset’s life.
By categorizing threats using this framework, you can identify and prioritize the key threats to your assets and develop a more targeted and effective maintenance strategy. With older assets, there is often so much focus on time-dependent threats, such as corrosion, that other potential threats, which may be more likely to cause failure, are overlooked.
For example, equipment like a pressure-regulating valve (PRV) is critical to the safe operation of penstocks. Failure of a PRV due to lack of maintenance could lead to a short-duration pressure increase that causes much higher stresses in the pipe than the wall loss due to corrosion might have, underscoring the importance of identifying and prioritizing key threats.
3. Manage the Threats
Once you clearly understand your assets and associated threats, the next step is to develop a program to manage the threats. Operation and maintenance should be critical components of your program. As I described earlier, it might be more cost-effective to maintain a PRV to manage pressure excursions than to replace corroded pipeline sections to achieve the same level of risk reduction.
Many penstocks and other water conveyance systems are well beyond their intended design life, but this doesn’t automatically mean they should be replaced. The primary time-related threat to steel pipes is corrosion. With proper inspection and maintenance, you can significantly extend the useful life of these assets. Regular inspection and repair of interior and exterior paint on above-ground penstocks or maintaining cathodic protection systems for buried pipes can add 30 to 50 years of reliable service. Read more about designing a maintenance program in “Crafting the Blueprint of a Power Plant Maintenance Program”, a blog by my Gannett Fleming hydroelectric colleagues Randy Bowersox, PE, and Jonny Rogado, PE, SPRAT I.
To craft a comprehensive maintenance program, consider leveraging resources from various industries that also use steel pipes. In addition to the American Society of Civil Engineers and American Water Works Association guidelines, other valuable resources include:
- Gas transmission industry codes: Similar to the challenges faced by water conveyance systems, gas pipelines require meticulous maintenance and threat management.
- Power plant and process industry manuals: Manuals like those from the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) can offer insights into best practices for maintaining large-scale infrastructure and evaluating degradation.
For example, ASME provides guidance for evaluating localized pitting, and a joint ASME/American Petroleum Institute document offers guidelines for assessing the fitness-for-service of steel pipes. The Centre for Energy Advancement through Technological Innovation has developed a penstock maintenance and repair reference manual.
Extending Asset Lifespan
Effectively managing water conveyance systems involves knowing your assets, understanding their threats, and developing and implementing a program to manage those threats. By leveraging existing resources from other industries and maintaining regular inspections, you can extend the lifespan and reliability of these critical components and support your hydroelectric system for many years to come.
Watch My INSIGHTS Webcast
For more tips and ideas, tune in to my INSIGHTS webcast, live on August 22, 2024, or on-demand thereafter. This webcast will delve deeper into the strategies and techniques for managing water conveyance systems and share perspectives from industry experts. You can also earn one professional development hour (PDH) for participating live or on-demand. I hope to see you there!
Featured Projects
EXCELLENCE DELIVERED AS PROMISED®
Hawaiian Dam Safety Seismic Hazard Assessment
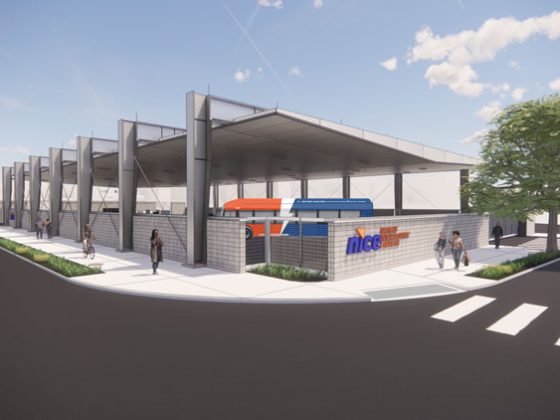

Nassau Inter-County Express Battery Electric Bus Charging
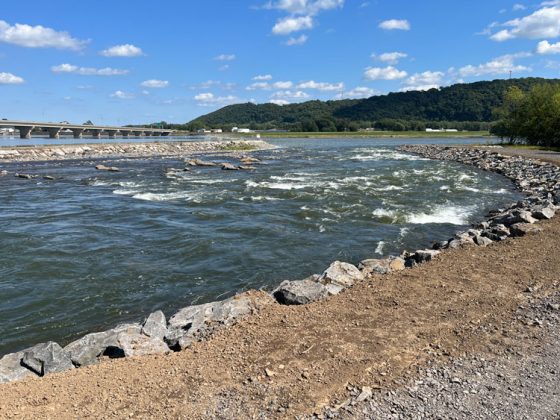

Fish Passage Design at the Adam T. Bower Memorial Dam
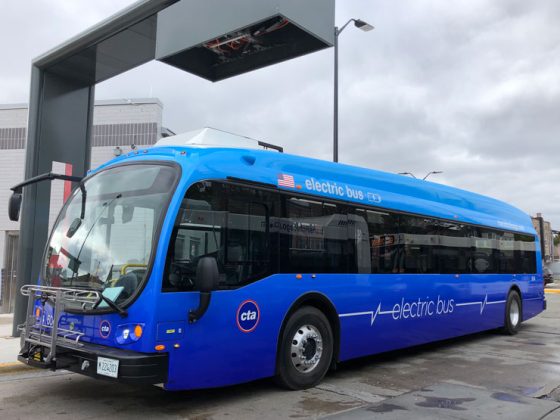

Zero-Emission Fleet Planning for the Chicago Transit Authority (CTA)

EEW Group Wind Energy Monopile Manufacturing Facility

Wildlife Refuge Dam Decommissioning and Sediment Management

New Jersey Transit Substation Recovery Program

Hydropower and Power Distribution Facilities Security Risk Assessment
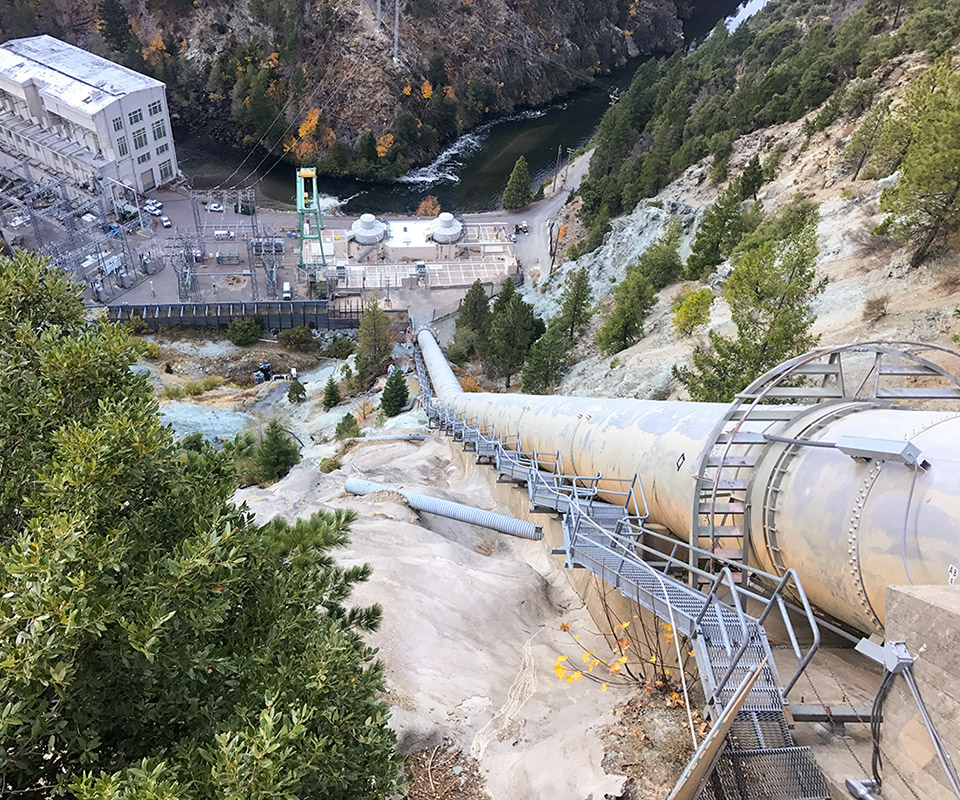

Hydroelectric Plant Penstock Data Acquisition System Upgrade
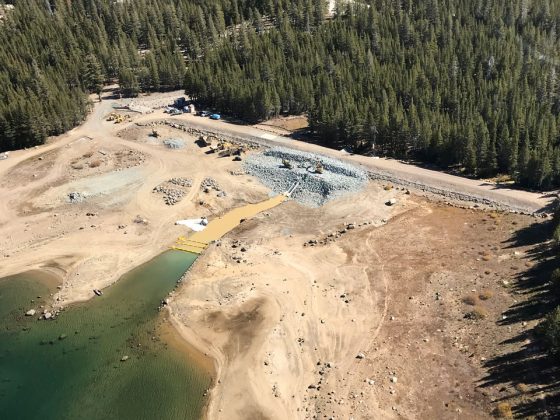

Upper Blue Lake Dam Seismic Retrofit Project
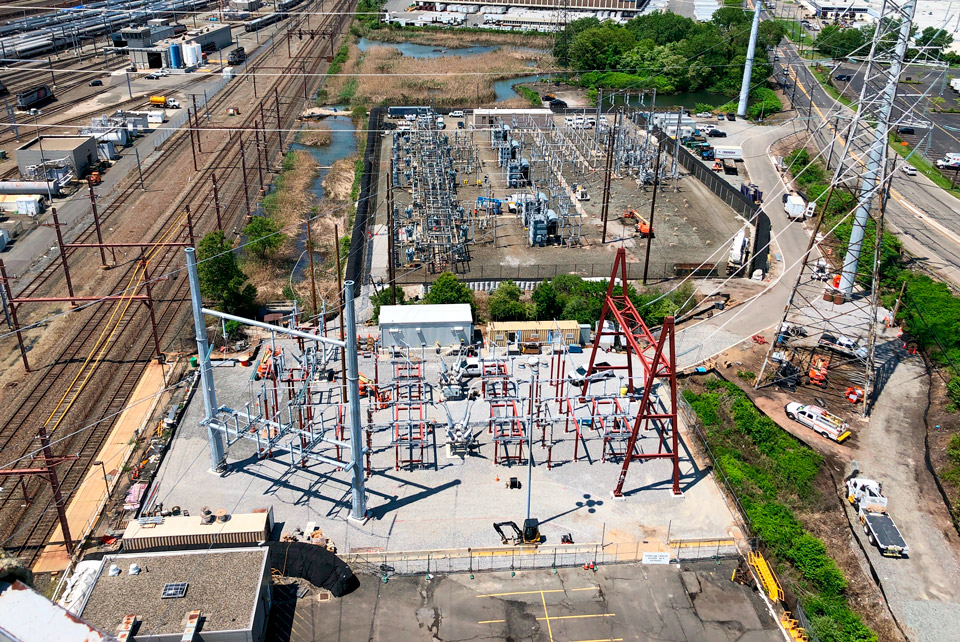

Meadows Maintenance Complex Supply Switching Station



























